The gas fees of Ethereum are at historic lows after the Dencun update, but they remain subject to variations related to network congestion and Layer 2 activity.
Key Points
- The gas fee of Ethereum measures the computational cost of each operation on the network.
- After the Dencun update, the average fees plummeted by 95%.
- Transactions now cost on average less than $0.50, but remain variable.
- Layer 2 continue to alleviate mainnet traffic, reducing costs.
- Factors such as MEV, contract complexity, and congestion influence the fluctuations.
What is the Ethereum gas fee and how does it work
The gas of Ethereum represents the unit that measures the amount of computation required to perform operations on the blockchain: transfers of ETH, DeFi interactions, or execution of smart contracts.
After the reform introduced by the EIP-1559, each transaction includes two main components:
- Base fee, automatic and burned at every block;
- Priority fee (or tip), an optional incentive for validators.
The cost formula is therefore:
Cost = Gas used × (Base fee + Priority fee)
The potential excess over the user’s set max fee is refunded, improving the predictability of expenses.
Ethereum Gas Fees Today: Record Decline in Numbers
After the Dencun update in March 2024, the network experienced an unprecedented drop in the average transaction cost.
- The daily average of gas has dropped from 72 gwei to 2.7 gwei, with a savings of 95%
- In monetary terms, a typical transaction has gone from $86 to approximately $0.39.
- According to YCharts, the average gas price fluctuates today around 3 gwei, with a block limit of approximately 45 million units.
- BitInfoCharts indicates that the average fee at the time of writing is equivalent to 0.00012 ETH, or about $0.52.
These are the lowest levels recorded since the transition to Proof-of-Stake in 2022.
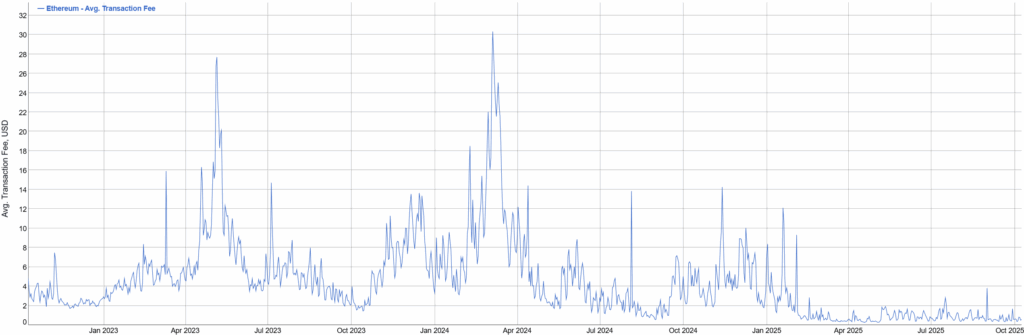
Why Ethereum Gas Fees Vary: Key Factors
- Network congestion
When transactions increase — for example, during a token launch or an NFT boom — the base fee rises. - Complexity of operations
Heavier smart contracts require more gas compared to simple ETH transfers. - Chosen priority level
Users can offer a higher tip to speed up the confirmation. - Role of Layer 2
Solutions like Arbitrum, Optimism, and zk-Rollups are diverting traffic from Layer 1, keeping fees low and the network more scalable. - MEV Activity and Transaction Reordering
The strategies of front-running or sandwich trading influence the distribution of fees and the incentive of validators.
When to Use Ethereum
- Recommended time slots: nighttime UTC and weekends, when global activity is reduced.
- Real-time monitoring: tools like Etherscan Gas Tracker or Blocknative allow you to check congestion.
- Layer 2 Solutions: for swaps or frequent transactions, rollups reduce fees by 10-50 times.
Optimizing Gas Fees for Developers and Users
Developers can reduce costs by avoiding redundant functions or inefficient loops in Solidity contracts.
Analysis tools like PeCatch identify areas of “gas waste” and allow saving up to 30% of transaction costs.
Users, on the other hand, can use wallets that automatically estimate the optimal fee based on the network (e.g., MetaMask or Rabby).
Analysis: Ethereum Cheaper but Still Sensitive to Demand
The drop in fees after Dencun marks a historic milestone for the network’s sustainability.
However, Ethereum gas remains a dynamic metric, subject to sudden spikes in case of market hype or intensive trading activity.
The structural cost reduction, combined with the expansion of Layer 2, is bringing Ethereum closer to a technological maturity phase: more efficient, but still strongly correlated to usage demand.
Today, Ethereum gas costs less than ever, with transactions under a dollar and a more scalable network.
However, volatility remains a constant: congestion, MEV, and DeFi traffic can still double the fees in a matter of minutes.
Ethereum thus continues its run towards a balance between economic efficiency and decentralization, paving the way for the next wave of Web3 adoption.